News and Announcements
- February 20, 2026
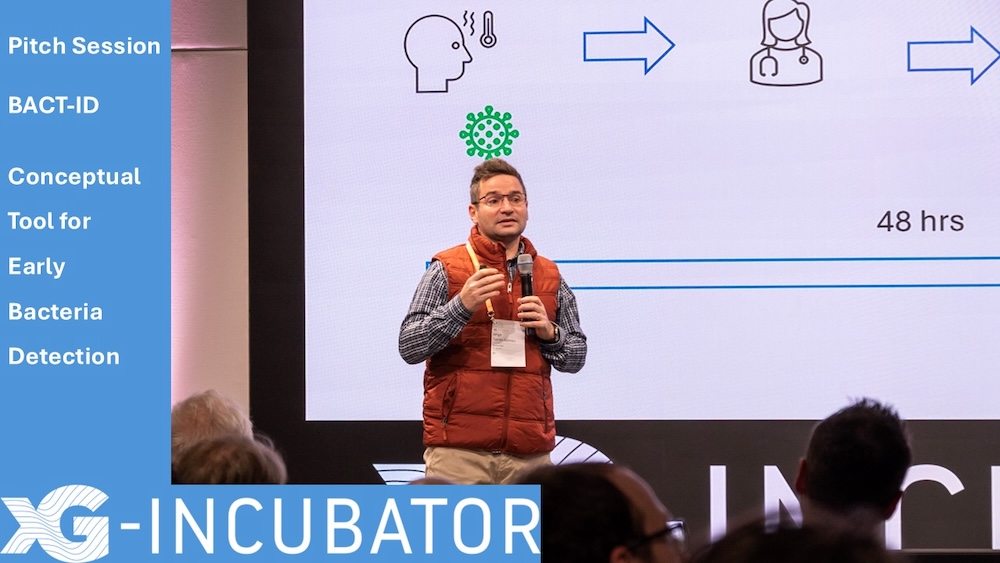

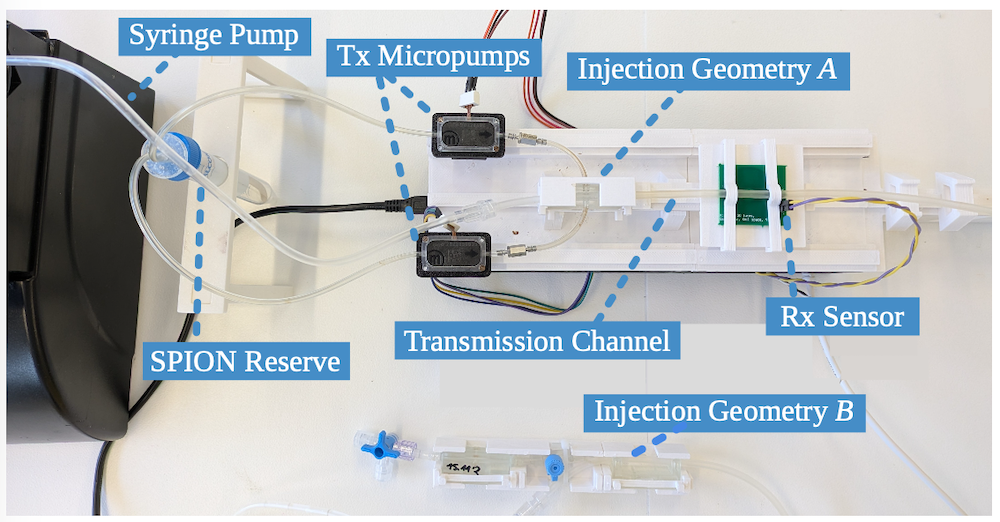
At the xG-Incubator networking event, our team member Jorge Torres Gómez presented the BACT-ID device concept, a microfluidic circuit for early detection of bacterial infections. The core idea is to embed physical signal processing directly into the geometry of a microfluidic chip, allowing it to amplify weak biomarker signals without increasing power consumption or system complexity. The concept integrates micro-sampling, BioFET sensing, and Bluetooth connectivity into a portable device. We aim to significantly improve sensitivity while reducing false positives to enable faster, more reliable detection of pathogen-specific biomarkers. Such a device would be used for applications including wound monitoring, sepsis screening, and antibiotic testing.
- February 20, 2026

We welcome Dr. Dilara Aktas who joined our group in February 2026.
- February 17, 2026
Falko Dressler gave a plenary talk titled Virtualized Edge Computing: Bridging Communications, Computing, and AI at the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC 2026), which was held in Maui, HI.
(link to more information)
- February 16, 2026

Our article Fed-Grow: Federating to Grow Transformers for Resource-Constrained Users without Model Sharing has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems.
The growing resource demands of large-scale transformer models pose significant challenges for resource-constrained users, particularly in distributed environments. To address this issue, we propose a federated learning framework called Fed-Grow, which enables multiple participants to collaboratively learn a lightweight scaling operation that transfers knowledge from pretrained small models to a large transformer model. In Fed-Grow, we introduce the Dual-LiGO (Dual Linear Growth Operator) architecture, consisting of Local-LiGO and Global-LiGO components. Local-LiGO addresses model heterogeneity by adapting each participant’s pre-trained model to a common intermediate form, while Global-LiGO facilitates knowledge sharing across participants without sharing local models or raw data, ensuring privacy preservation. This federated approach offers a scalable solution for growing large transformers in a distributed manner, where only the Global-LiGO is shared, significantly reducing communication overhead while maintaining comparable model performance under the same communication constraints.
(link to more information)
- January 09, 2026
TKN presented two tutorial lectures at the IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC 2026), which was held in Las Vegas, NV.
Doğanalp Ergenç and Nurefşan Sertbaş Bülbül talked about IEEE 802.1 Time-Sensitive Networking Beyond Theory: Convergence, Resilience, and Practical Insights.
In parallel, Falko Dressler and Onur Altintas talked about Cooperative Computing and AI on Cars using 6G Virtualized Edge Computing.
- January 09, 2026

Falko Dressler gave a keynote titled Virtualized Edge Computing for Resilient Edge-AI at the 1st International Workshop on AI-Native Connected Mobility (ACM 2026), which was held in Las Vegas, NV.
(link to more information)
- January 05, 2026

We are happy to be part of the xG Research and Innovation Cluster (xG-RIC).
In this project, we will explore AI-native ORAN solutions, channel prediction techniques, the use of intelligent reflective surfaces, and advanced edge computing.
(link to more information)
- December 30, 2025

Our article Fed-RAA: Resource-Adaptive Asynchronous Federated Edge Learning with Theoretical Guarantee has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing.
This paper studies an efficient federated learning (FL) problem involving multiple edge-based clients with heterogeneous constrained resources. Compared with numerous training parameters, the computing and communication resources of clients in edge scenarios are usually insufficient for fast local training and real-time knowledge sharing. Besides, training on clients with heterogeneous resources may result in the straggler problem, which delays the convergence of FL. To address these issues, we propose Fed-RAA: a Resource-Adaptive Asynchronous Federated learning algorithm. Different from vanilla FL methods, where all parameters are trained by each participating client regardless of resource diversity, Fed-RAA adaptively allocates submodels of the global model to clients based on their computing and communication capabilities. Each client then individually trains its assigned submodel and asynchronously uploads the updated result. Theoretical analysis confirms the convergence of our approach. Additionally, an online greedy-based algorithm is designed for asynchronous submodel assignment in Fed-RAA, improving the convergence of Fed-RAA by optimal minimization on the training delay bound of submodels. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, our Fed-RAA algorithm reduces the time required to achieve the target accuracy by an average of 30.89%, demonstrating its superior efficiency on heterogeneous constrained computing and communication resources. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first resource-adaptive asynchronous method for submodel-based FL with guaranteed theoretical convergence.
(link to more information)
- December 16, 2025
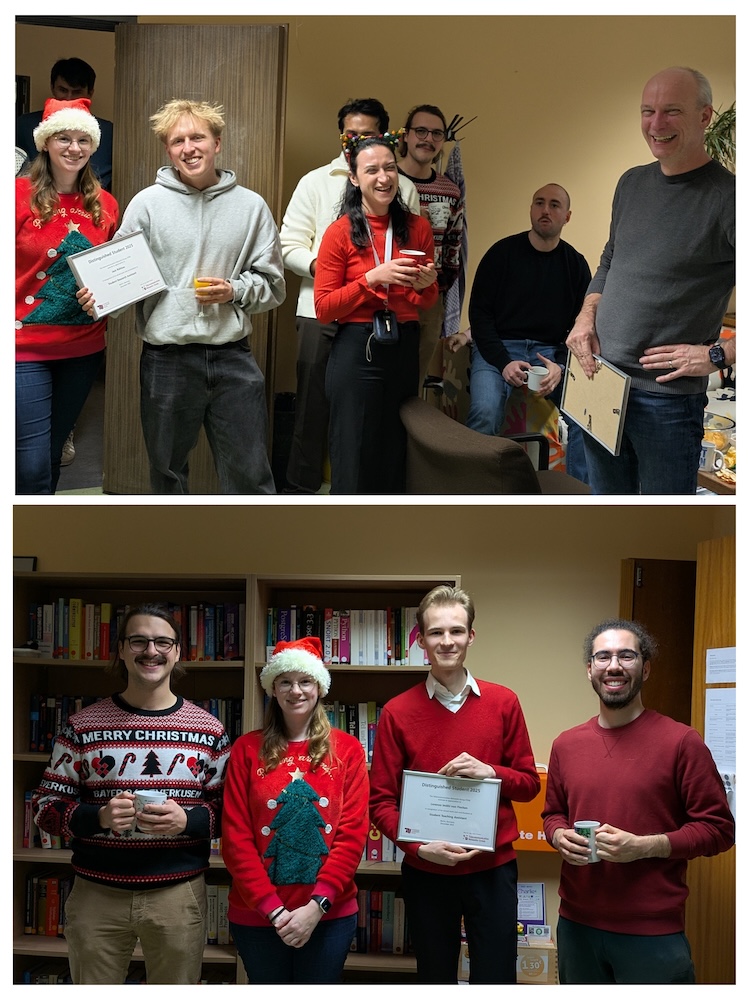

We congratulate Jakob Rühlow and Lorenzo Imöhl von Flocken for receiving this year's Distinguished Student award at TKN! With the the award, we recognize their valued work and contributions as Student Research Assistant and Student Teaching Assistant, respectively.
- December 16, 2025
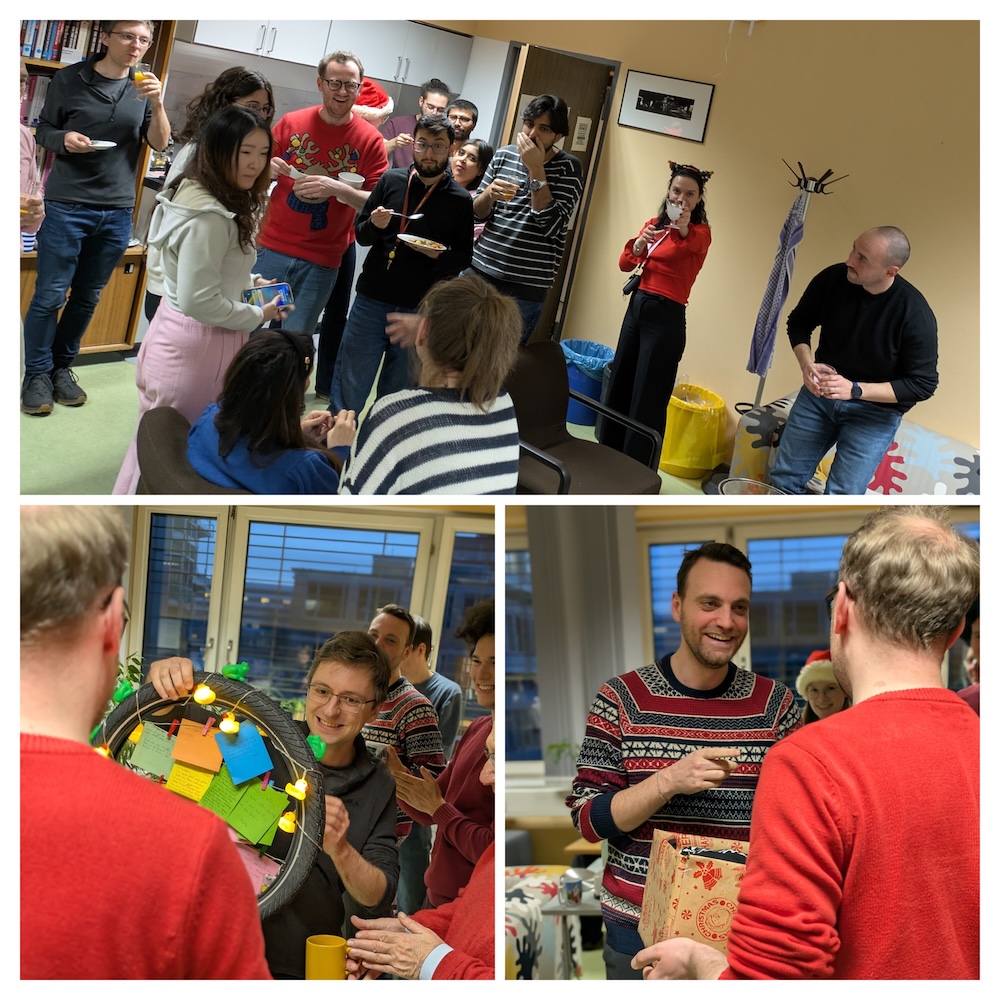

The end of the year is near again.
Today at TKN, we celebrated a successful 12 months reading and writing interesting papers, being part of inspiring teaching moments and meeting amazing new colleagues.
We enjoyed a relaxed celebration and are grateful for our amazing team.
Now, we wish all of our friends, collaborators, and followers a wonderful Christmas time, a good end to the year 2025 and a Happy New Year!