EWI - Energy efficient WLAN for IoT

Institutions
- Paderborn University
- TU Berlin
- Software AG
Team @ CCS
- Johannes Blobel (PI)
- Prof. Dr. Falko Dressler
- Anke Küstner
- Mohness Waizy
- Luca-Sebastian Henke
Funding
- BMBF

Project Time
- 11/2018-05/2021
Description
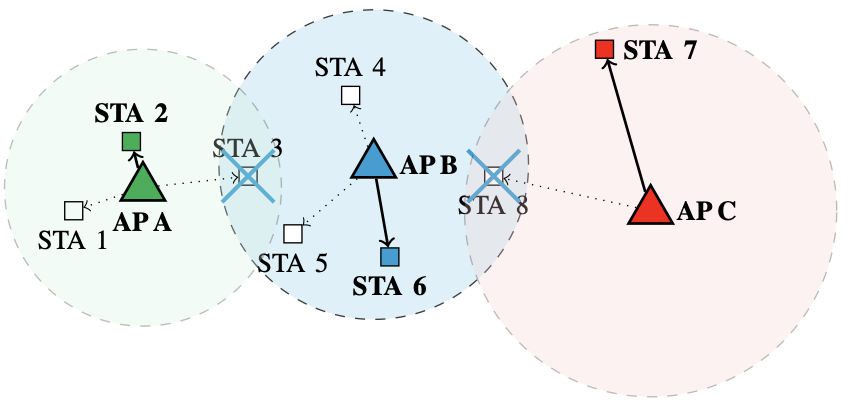
In recent years wake-up receivers have shown to be a promising technique to achive ultra-low power communication in wireless sensor networks. In this project we study the feasibility of using this technique to make Wireless LAN (WLAN) more power efficient. Instead of using the duty-cycling approach of the normal power save mode, we add an additional wake-up receiver to the mobile stations. If an accesspoint gets new data for a station in sleep mode, it can use this receiver to wake the station up and immediately send the packets. This technique achieves lower power consumption and lower delays compared to existing solutions. We study our proposed system by building hardware prototypes in conjunction with extensive simulations.
Selected Publications
2022
Journals and Magazines
 Johannes Blobel, Florian Menne, Dongxiao Yu, Xiuzhen Cheng and Falko Dressler, "Low-power and Low-delay WLAN using Wake-up Receivers," IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 21 (5), pp. 1739–1750, May 2022.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Johannes Blobel, Florian Menne, Dongxiao Yu, Xiuzhen Cheng and Falko Dressler, "Low-power and Low-delay WLAN using Wake-up Receivers," IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 21 (5), pp. 1739–1750, May 2022.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
2021
Conferences and Workshops
 Johannes Blobel, Vu H. Tran, Archan Misra and Falko Dressler, "Low-Power Downlink for the Internet of Things using IEEE 802.11-compliant Wake-Up Receivers," Proceedings of 40th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM 2021), Virtual Conference, May 2021.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Johannes Blobel, Vu H. Tran, Archan Misra and Falko Dressler, "Low-Power Downlink for the Internet of Things using IEEE 802.11-compliant Wake-Up Receivers," Proceedings of 40th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM 2021), Virtual Conference, May 2021.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]